|
Our feet are where the body contacts the floor/earth. Every ounce of our body's weight goes through them with each step, whether we have a light step or plod heavily. So they are vitally important to our physical health. Poorly functioning feet lead to a poorly functioning body much the same way that damaged wheels make a poorly functioning car.
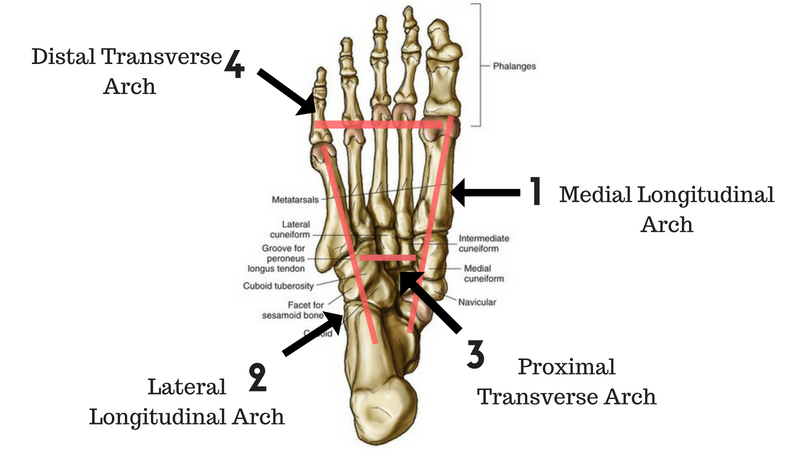
We have all heard of "flat feet," where the inside arch of the foot collapses toward the floor, often creating painful repercussions in the ankle, knee, hip and even back. This condition commonly refers to just one of the arches of the foot---of which there are four---the medial longitudinal arch (labeled above, #1). That is a fancy way of saying the lengthwise (longitudinal) arch on the inside (medial) of the foot. Most of us just know it as the "arch." This well-known arch of the foot is not structured like a weight-bearing arch. It is built more like a spring that bends when we put weight on it and bounces back as we release. This is how some of the "spring in our step" occurs, as the arch recoils. This arch can be bolstered with muscular strength, like lifting the inner ankles up and pulling the ball of the foot toward the heel. The second major arch of the foot is the lateral longitudinal arch, which means the lengthwise (longitudinal) arch on the outside (lateral) of the foot. It is labeled in the picture above with #2. This arch goes from the heel area toward the pinky toe. It is a very stable arch, with bone structure like a traditional weight-bearing arch. Due to its structure, this arch rarely collapses or gives us trouble, so we don't even realize it's there. The third arch of the foot goes across the foot, so it is called a transverse arch. Since it is closer to the ankle, it is called the proximal (near to the body) transverse arch, labeled #3 in the picture above. This arch, like #2 above, is structurally very stable and rarely collapses or gives us trouble. This arch is also called the anterior (forward) transverse arch. The fourth arch of the foot is sometimes not considered an arch at all because it is not formed by arch-like bony structures. Instead, this arch is made of soft tissues like ligaments, muscles and fascia, stretching from the big toe to the baby toe. It is called the distal (far from the body) transverse arch, labeled #4 in the picture above. Since it is not a bony-structured arch, this often gives us trouble due to weakness and under-use, especially since we wear shoes that decrease our body's need to access it. It can be strengthened though simple exercises like making fists with the toes. Try standing with bare feet. Shift your weight around your feet, from front to back and side to side. Pay close attention and see if you can feel the arches and structures in your feet. They are important!
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AUTHORSScott & Ida are Yoga Acharyas (Masters of Yoga). They are scholars as well as practitioners of yogic postures, breath control and meditation. They are the head teachers of Ghosh Yoga.
POPULAR- The 113 Postures of Ghosh Yoga
- Make the Hamstrings Strong, Not Long - Understanding Chair Posture - Lock the Knee History - It Doesn't Matter If Your Head Is On Your Knee - Bow Pose (Dhanurasana) - 5 Reasons To Backbend - Origins of Standing Bow - The Traditional Yoga In Bikram's Class - What About the Women?! - Through Bishnu's Eyes - Why Teaching Is Not a Personal Practice Categories
All
Archives
May 2024
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed