|
Hardly a day goes by when someone doesn't ask us, "Is Bikram Yoga the same as Ghosh Yoga?" It is a valid and interesting question, as plentiful yoga systems seek to separate themselves from the competition with novel methods and attributes. The two methods are closely related, since Bikram Choudhury learned at Ghosh's College. But there are some fundamental differences that keep the two systems from being synonymous.
First, let's look at what they have in common. THE POSTURES Most of the exercises in Bikram Yoga are recognizably from the Bengal region of India, where Ghosh's College is located. The previous students of Ghosh taught these same postures and exercises like Half Tortoise, Rabbit and Standing Head to Knee. And several of the postures, like Stretching, Cobra, Locust, Bow and Corpse, are traditional yoga asanas found in older texts. Notably missing from both Bikram and Ghosh yogas are exercises like Up-dog, Down-dog and Warriors One and Two which come from South India and have made their way into most vinyasa yoga styles. STILLNESS Another element shared between Bikram and Ghosh yogas is the alternation of effort and rest. Each posture is held in stillness for a brief period and followed by an equal portion of relaxation. While standing, the practitioner simply stands still, though some of the older Ghosh students insisted on lying down between exercises. During postures on the floor, relaxation happens by assuming the Corpse posture. This is a distinctive element of these styles, setting them apart from the popular flowing methods that link stationary positions with fluid movements and Sun Salutations. THERAPEUTIC INTENT It can seem obvious, but both Bikram and Ghosh yogas are fundamentally designed to help the student be healthy. This is similar to all the yoga in Bengal, where the postures are done to help the organs, circulation, digestion or some other element. They generally have a therapeutic purpose. This intention can be contrasted with many vinyasa styles of yoga that originated in the performative gymnastics of Mysore. Those styles, like Ashtanga Vinyasa and its descendant "flow" methods, have become more therapeutically focused over the ensuing decades. But the origin of flowing yoga was performative. Now, let's look at what is different between Bikram Yoga and Ghosh Yoga. SET INSTRUCTIONS The method of Bikram's yoga is largely defined by its style of instruction, the rote utterance of prewritten commands. Teachers of the style can be judged by the quality of their "dialogue." Many paraphrases and copycats have popped up, but Bikram's original is still considered by most to be the gold standard. This rote instructional style is nowhere present in the teachings of Ghosh Yoga, where the majority of verbal instruction is simply counting the duration of each exercise. HEAT Also central to Bikram's style is a heated room, a characteristic that finds no expression in other manifestations of Ghosh's style. In India, they turn on fans or air conditioning when the day gets hot, or they forego the scorching parts of the day altogether. A SET SEQUENCE The two differences above are somewhat peripheral to the essence of the methods. The irreconcilable difference between these two systems is Bikram Yoga's unchanging set of exercises. The same 26 postures are "prescribed" for every student no matter their age, ability, experience, goals or ailments. Central, indeed fundamental, to the Ghosh system is a unique prescription for each student. It would be unheard of to assign the same practices to different people, especially without learning their strengths and weaknesses. Because Bikram Yoga is defined by its specific and repeated set of postures, and Ghosh Yoga is defined by its attention to the individual, it is impossible to conclude that Bikram Yoga and Ghosh Yoga are the same thing. They certainly share several key elements, namely their postures, the alternation of effort and relaxation, and therapeutic intent. But the defining characteristics of Bikram Yoga like rote instruction, added heat and especially a single unchanging set of exercises separate it substantially from Ghosh Yoga.
3 Comments
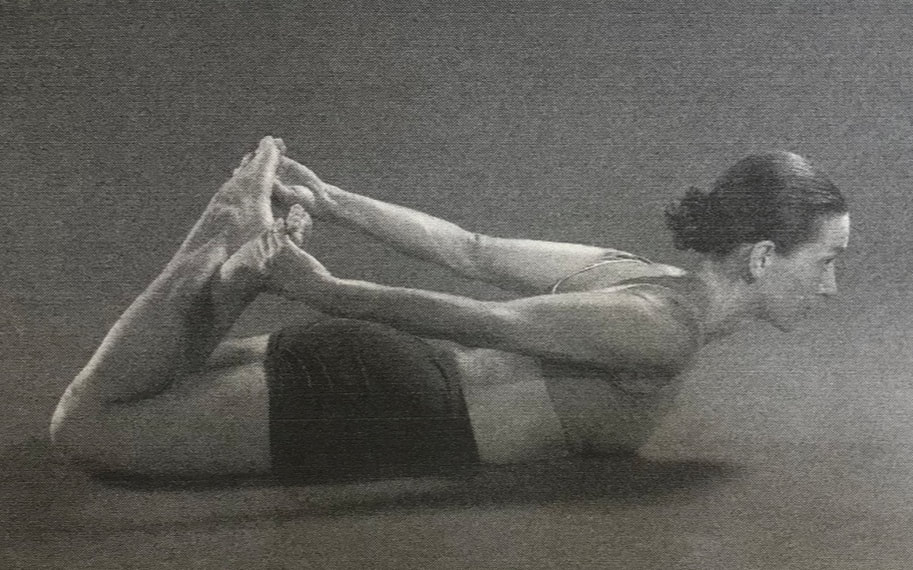
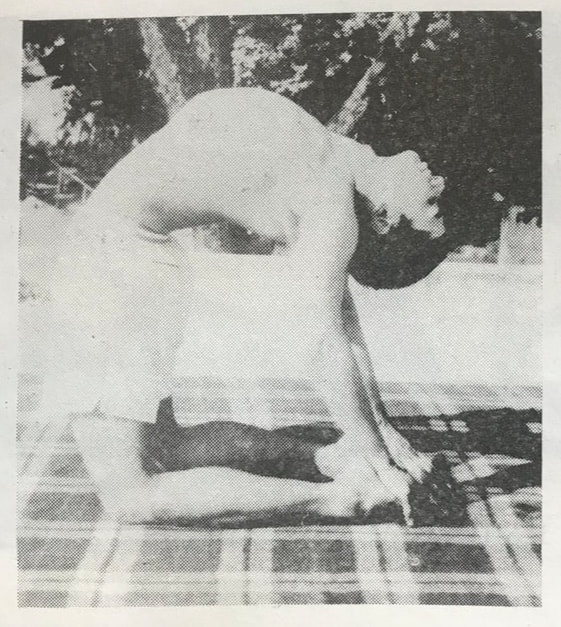
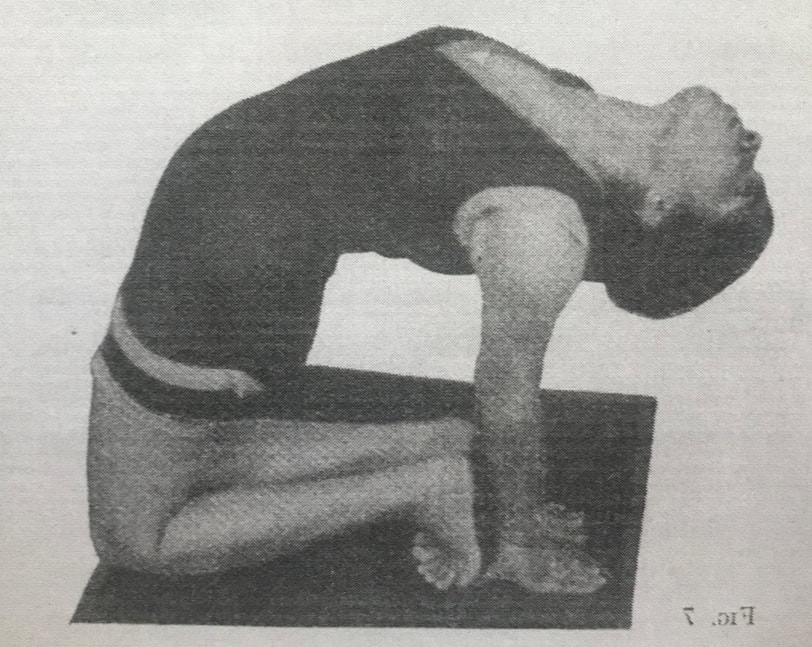
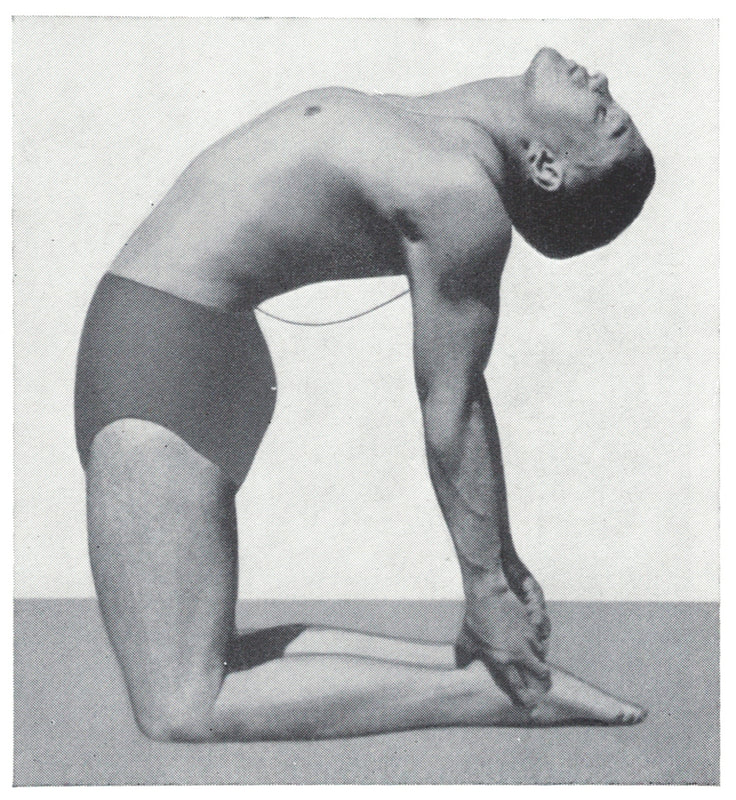
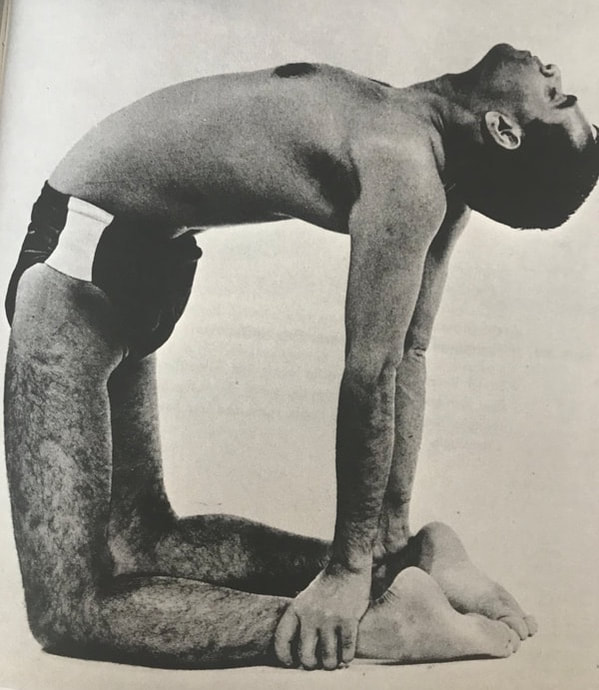
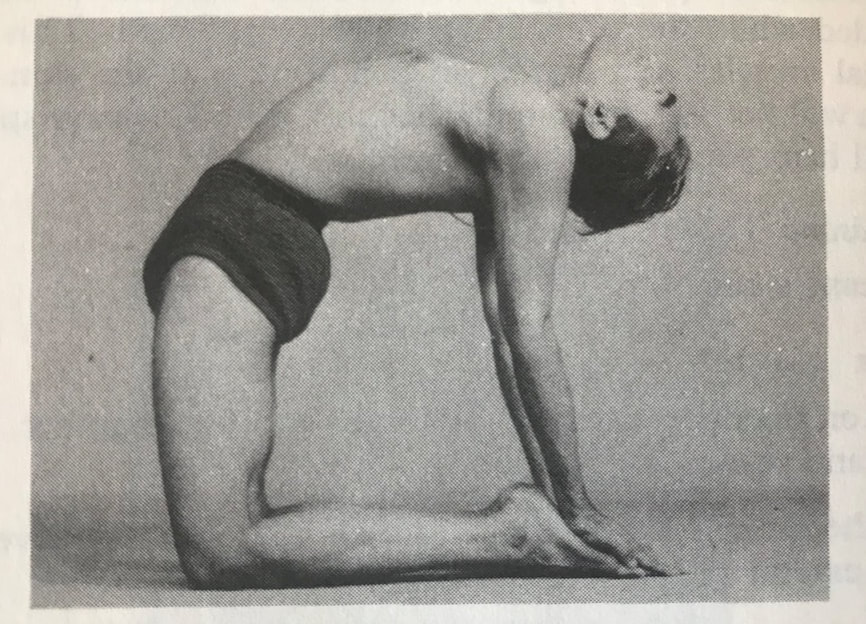
Camel Posture, Ushtrasana, has at least 300 years of history in yoga texts. But the posture changed drastically in the mid-20th century from the traditional prone position (as pictured above) to the kneeling backbend that most modern yogis will recognize. This shift from prone to kneeling happened over the course of a few decades between 1920 and 1960. Prior, Camel Posture was a posture done on the belly. After 1960 it is done on the knees. In between, one might find instruction for either. Below we have elaborated 8 versions of the posture that show its irregular progression through these decades.
Buddha Bose (1938): Bose instructs the posture as in the Gheranda Samhita, lying on the belly. Like many of his other instructions, Bose draws directly from Sivananda, comparing the posture to Dhanurasana, Bow Posture. Sadly, Bose does not have a photo. "Lie on the abdomen...bend the legs backward from the knees...with the hands firmly grasp the ankles. Now lift the head." The only difference between the two postures, he says, is "do not raise the knees and thighs off the floor" in Camel.
IN CONCLUSION
It is possible that these two positions are unrelated, connected only by their name. It is difficult to explain why the abdominal Camel Posture was phased out at the same time as the kneeling Camel Posture was phased in. Since about 1960, the kneeling version is ubiquitous. But the older texts including the Gheranda Samhita and those by Sivananda, Buddha Bose and Yoga Mimamsa clearly instruct the same position, lying on the belly with crossed legs. Sita Devi's book from 1934 is the outlier here, with instruction of the kneeling version in such an early decade. Also difficult to explain is the divergence between Bose and Mukerji, who were both students of BC Ghosh in Kolkata. In the 1930s, Bose describes Camel as lying on the belly, while Mukerji does it kneeling only 30 years later in 1963. When we practice yoga postures, we might be doing them for different reasons. We may be trying to reduce the pain in our backs, improve our balance, burn a few calories or experience a deeper spirit within. These are drastically different goals, and we can't use the same techniques to achieve them all. Hundreds of "yoga" postures and practices exist these days, and they don't all attain the same things. As you practice, think carefully about what you are trying to accomplish, and use those postures that will help. Here are the 5 different types of yoga postures:
1. Seated, meditation postures. These are the oldest, most traditional yoga postures. When the Yoga Sutras (or any text that is more than 1,000 years old) refer to asanas, this is what they mean: a seated, upright, stable and relaxed position. These positions are not used for their own benefit or to create health, but to facilitate the more internal practices of breath control and meditation. These are the quintessential "yoga postures," Lotus and Siddhasana. 2. Positions to prepare the body for seated meditation or help the body recover from it. As anyone who has tried to sit still for a long period of time knows, it is difficult for the body. A certain amount of flexibility is required in the hips and knees, and some strength and control is required in the spine. How does one build these? Several positions, usually seated, were propagated in early hathayoga to help the body prepare for sitting or recover from the imbalances that arise during sitting. These postures include Cowface, Butterfly, Cobra, Bow and Locust. These are some of the first non-Lotus postures. 3. Anti-gravity postures. Influenced by tantra, hathayoga had many practices that were designed to prevent the precious bindu from dripping out of the head and into the abdominal fire. This was thought to improve vitality, spiritual potency and life. This is where we get the practices that turn the body upside down or "draw upward" the energy, winds or fluids of the body. Headstand, Shoulderstand, Mula Bandha, Uddiyana Bandha, and the upward-focused intention of many postures are intended for this purpose. 4. For physical health. These postures and exercises are much more recent, often coming from calisthenics, gymnastics and wrestling. They build strength, flexibility and health in the body. There are lots of different positions that affect varied parts of the body, so they are vast and diverse. Kuvalayananda called these "cultural" postures. These have become central to the practice of modern yoga. 5. For demonstration and impressive accomplishment. From ancient times, yogis have been associated with the ability to do remarkable feats. In the last couple hundred years, that has increasingly meant physical demonstrations of balance, endurance, strength and flexibility. Influenced by the developments of gymnastics, acrobatics and contortion, these practices include Splits, Handstand and most arm balances. This tendency toward outwardly impressive beauty has been compounded with the rise of photography, the internet and visual communication media like Instagram. Who doesn't love to see a beautiful, impressive picture of a body? One type of posture is not better than the others. There is no hierarchy here, though as yogis some danger lies in focusing on the body and in cultivating techniques for display. Worth noting is that postures can have drastically different purposes, goals and intentions. When we practice them, we should know what we are practicing so we can move in the right direction. Along with the introduction of modern physical practices, a lot has been lost in the world of breath control practices as they were documented through yogic texts for many hundreds of years. Pranayama is most easily translated as breath control, but “prana” means one’s life force. Pranayama is therefore, the control of one’s life force as accessed through the breath.
There are many benefits to controlling the breath. These benefits continue to be brought to the forefront through scientific study. Benefits range from relaxation to potentially suppressing tumor growth in the body. While the studies are magnificent in their potential, the most powerful reason to cultivate the breath in yoga is because of its intermediary relationship to the body and the mind. When we access and manipulate the breath, we use two different parts of our brain. We also can access the two parts of our autonomic nervous system by changing how we breathe. If that wasn’t enough, we can also choose which nostrils we breathe through and stimulate our olfactory nerve which has a direct relationship with our brain. Many of us might question the necessity of these types of practices since our breath is an automatic function. However, it is easy to make the judgement that breath manipulation is unnecessary when we have not experienced the results. Once you realize breathing can reduce stress, focus the mind, and possibly suppress cancerous tumors, it seems an obvious practice to undertake. When we strengthen our awareness of the body through asanas, we are mostly concerned with our muscles, bones and structural tissues. We get stronger muscles, and ease muscular tension. The benefits often translate into other systems of the body which result in things like better circulation or digestion. However it is not until we get into pranayama that we experience the body on a deeper plane. The awareness we get from breathing is the awareness of our nervous system. It is a deep and profound level of awareness that leads us to a level untouched by most: experiencing the mind. Most of the time we experience our thoughts. We never think about thinking, we only react to our thoughts. We get lost in the result of our thoughts, but not in what caused them to begin with. A very common example of this phenomenon involves the idea of a movie and the screen on which the movie is projected onto. When we watch a movie, we know it is not real. The screen is blank before the movie begins and is blank after the movie finishes. We just accept this. However our minds are no different! They are blank before a thought arises and blank after the thought finishes. The problem is that we mistake the thoughts for reality. Through stillness, we can learn to identify the “movie screen” of our minds as reality, not the fleeting thoughts that project onto our mind. Pranayama, and working to still the breath, is the gateway into stillness of the mind. The body is the first step on the path of stillness. We must learn to make the body strong and energized while being calm and present. This is a type of strength and physicality we are not used to in the modern world.
In today’s world, the body is often thought of as an unfortunate and failing reality we have to deal with that must be conquered through mental will power, fitness, food, drugs or surgery. When the body doesn’t do what we think it should, we curse it, ignore it or cut it open. On the path of yoga, the body is a gateway toward realization, not an interruption. We might live with other people but we live in our body. If we cannot hear what our own body is telling us, it is hopeless to think we can make more subtle connections with what we think or who we are. If we cannot connect with our body, how will we connect with anyone else? If we cannot feel the harm we do to ourselves, we will never comprehend the harm we do to others. Our body is a source of strength that we can tap into, but we must treat it as such. With time, the strength we cultivate in the body will lead us to realize we can stand still in the middle of our lives and wait for the answers we are looking for. There are many ways to make the body strong, like weight lifting, running and calisthenics. But yoga is unique in its ability to teach awareness of the body. On the path of yoga, we begin by putting the body in physical positions called postures or asanas. Each posture has a set of physical benefits. They require distinct combinations of strength and flexibility. The benefits surface when we contract and relax the muscles as prescribed in each asana, while bringing stillness into the body and mind. In this way, we feel exactly what comes up in the body and learn to relax around it. In asana, we learn to sift through pain, injury, exhaustion, ego, drive, focus, tension and countless other fluctuations that surface when experiencing the body. The body is the first way in which we associate with the power of stillness. Through the body, we learn how to listen. We learn how to work in harmony with the tools we have, not in a state of inner conflict. If we cannot listen to the body, we cannot listen to the breath, and we certainly cannot listen to the mind with any deep level of awareness. |
AUTHORSScott & Ida are Yoga Acharyas (Masters of Yoga). They are scholars as well as practitioners of yogic postures, breath control and meditation. They are the head teachers of Ghosh Yoga.
POPULAR- The 113 Postures of Ghosh Yoga
- Make the Hamstrings Strong, Not Long - Understanding Chair Posture - Lock the Knee History - It Doesn't Matter If Your Head Is On Your Knee - Bow Pose (Dhanurasana) - 5 Reasons To Backbend - Origins of Standing Bow - The Traditional Yoga In Bikram's Class - What About the Women?! - Through Bishnu's Eyes - Why Teaching Is Not a Personal Practice Categories
All
Archives
May 2024
|
















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed